Overview
The ISN S8 can be used to measure the conducted voltage emissions of telecommunication and data processing equipment. It is designed to measure coaxial line. It is based on IEC/CISPR 22 and the related national standards. The special circuitry and design is described in CISPR 22, and EN 55022 Annex D figure D.9. The ISN must provide sufficient decoupling from the equipment under test (EuT) to the auxiliary equipment (AE) which could be a communication device or a kind of load. The measured conducted voltage is coupled out to the BNC connector on top of the ISN S1. An EMI receiver or spectrum analyzer is most commonly used for a measuring instrument.
The ISN S1 can also be used in the other direction to inject conducted radio frequency disturbance into the shield of communication wires. This method is described in IEC/EN 61000-4-6. If the ISN S8 is used for injection it is also referred to as coupling decoupling network (CDN).
Application
The measurement is described in detail in CISPR 22, CISPR 32 and EN 55022 chapter 8.
The equipment under test must be connected to the EuT-port. The auxiliary equipment has to be connected to the AEport. The EMI-receiver or spectrum analyser has to be connected to the BNC port of the ISN S1 using a coaxial line.
Fixture lugs at the bottom plate of the ISN S1 allow to fix the device with screws to the cabin wall.
As CISPR 22 defines the limits for conducted emissions in a 150 ? system there is an 100 ? resistor in series to the BNC connector. In combination with the 50 ? input resistance of the measurement device a voltage division factor of 1:3 follows. In a logarithmic scale this is equal to 9.5 dB. The measured voltages across 50 ? therefore has to be multiplied with 3 or in other words a correction of 9.5 dB must be added. This value of 9.5 dB is called the voltage division factor (VDF). This VDF is slightly frequency dependent. For very precise measurements it is recommended to take the exact frequency dependent VDF into account (see calibration certificate).
The shield or outer cable is defined as the common mode point for the EuT connector of ISN/CDN equipment.
ISN Voltage Division Factor

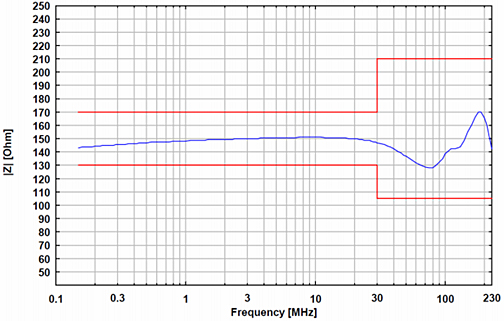
ISN Impedance (Magnitude)
| Specifications | |
| Nominal Frequency Range | 150 kHz – 230 MHz |
| Type of cable | Koaxial, 50 ? coaxial, 50 ? |
| Connector | BNC |
| Max. voltage line – ground | 150 V DC 100 V AC |
| Max. line current/path | 1 A DC |
| Common mode impedance EuTside 150 kHz – 30 MHz 30 MHz – 230 MHz | 150 ? ±20 ? 150 ? + 60 ?/-45 ? |
| Phase error | 0° ±20° |
| Measuring port | 50 ? BNC |
| Max. voltage measuring port | <20 V AC |
| Voltage divisions factor EuT – measuring port: 150 kHz – 30 MHz 30 MHz – 230 MHz | 9.5 dB ±1 dB 9.5 dB +4 dB/-2 dB |
| 3 dB transmission bandwith EuT – AE | >250 MHz |
| Dimensions W x H x D | >225 mm x 129 mm x 105 mm |
| Weight | ~1265 g |
| Acc. to standard | CISPR 22, Annex. D.9 CISPR 32, Annex. G.9 |







